Cardiac arrest is a deadly heart condition; here, the word arrest indicates stopping or bringing to an end. In cardiac arrest, the heart quits beating, and this situation is known as unexpected cardiac death. Electrical impulses control the heartbeat; when there is a variation in the pattern of impulses, the heartbeat becomes damaged, called an arrhythmia. If any below symptoms are shown, contact a doctor, online pharmacy, or buy medicine online drugstore delivery at your doorstep.
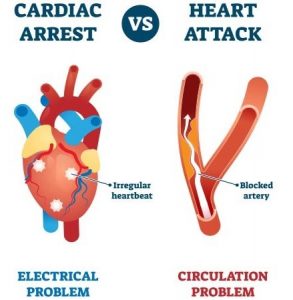
Causes Of Cardiac Arrest
Several circumstances can commence however, two of the essential factors include ventricular and atrial fibrillation.
-
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation is one of the most common causes. The heart has four chambers- these heart chambers shaking out of control. This creates the heart’s rhythm to reduce suddenly. In a few occurrences, the circulation of blood stops entirely, pointing to sudden cardiac death.
-
Atrial Fibrillation
The heart can stop beating instantly after an arrhythmia in the atrium. Atrial fibrillation occurs when the sinoatrial node doesn’t manage the heart and pumps the blood.
Also Read: Heartburn – All You Need To Know About Its Causes And Symptoms
Who Is At Risk For Cardiac Arrest?
- Smoking
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Family history of heart disease
- History of a previous heart attack
- Age over 45 for men, or over 55 for women
- Men are at high risk than women
Also Read: How Does Oral Health Determine Your Heart Health
What Are The Symptoms For Cardiac Arrest?
Initial symptoms are usually warning signs, and taking prompt treatment before the heart stops working can save your life. It may not have symptoms before it occurs; if you have symptoms that continue, inquire for urgent medical care.
Symptoms are direct and severe, which include:
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
- Heart palpitations
- Immediate emergency care is required if someone is experiencing these symptoms.
- Chest pain
- No pulse
- Difficulty breathing
- Loss of consciousness
- Collapse
When to see a doctor
If you experience any of these signs and symptoms consult your doctor immediately
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats
- Fainting or near fainting
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Unexplained wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
When the heart stops, it may cause death or constant brain damage within seconds or minutes.
How To Diagnose Cardiac Arrest?
Medical treatment is directed at getting the blood flowing back to the body. The surgeon will apply a defibrillator to shock the heart; an electric shock can mostly return the heart to a normal rhythm.
- Some of the separate tests done to fix for indications of a heart attack include measuring potassium, magnesium, hormones, and other chemicals that can harm the heart’s capacity to function.
- Chest X-ray permits the doctor to observe the size and shape of the heart and blood vessels. It may further show whether you have any heart stoppage.
- A nuclear scan test is usually performed with a stress test that serves to determine blood flow problems to the heart.
- Coronary catheterization is a method where a liquid dye is inserted into the heart’s arteries through a long thin catheter. As the dye loads arteries, it displays visible on X-ray and videotape, showing sections of blockage.
What Are The Treatments For Cardiac Arrest?
- It requires immediate medical care for survival.
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is one class of emergency treatment. Defibrillation is different and helps to get the heart beating newly again once it has stopped.
- A survived patient will be put on medicines to lower open blood pressure and cholesterol levels that may overcome the risk of another heart attack.
- Surgery may be required to repair damaged blood vessels or heart flaps that bypass or open blockages in the arteries.
- Dietary modifications and choosing a healthier lifestyle may serve to develop cardiac health and wellness.

 Login/Register
Login/Register









Be the first to comment on "Sudden Cardiac Arrest: Causes, Risk, Symptoms & Treatment"