When individuals communicate with each other about their blood pressure, it shows 2 different numbers, i.e., systolic and diastolic. While maintaining blood pressure with healthy diets and physical activity is necessary for good health. Try to take proper medicines for blood pressure as per doctor consultation, also measure pulse pressure regularly. You can get the online medicine delivery with same day priority delivery and with various discounts.
Table of Contents
What is systolic blood pressure?
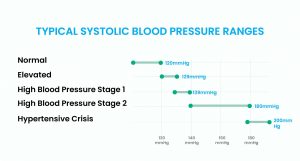
The systolic meaning defines the heart as urging blood out into the arteries. The term systole is also called systolic blood pressure. It’s the pressure through a heartbeat and the maximum pressure estimated. The systolic blood pressure is estimated average when the reading is 120 mmHg.
What is diastolic blood pressure?

The diastole term is also called “diastolic blood pressure.” The diastolic meaning defines the heart rate between beats so it can refill with blood. Diastolic pressure is the pressure during quiet rest as 80 mmHg is considered an average blood pressure.
The Blood Pressure Reading
- Your blood pressure reading is recorded in a composition: 120/80.
- It is pronounced: “120 over 80.”
- The systolic blood pressure reading is the higher number.
- The diastolic pressure reading is the lower number.
- The units are millimetres of mercury (mmHg).
Methods to maintain systolic and diastolic blood pressure?
A range of methods is available for diastole vs systole blood pressure. Here are the possible methods to treat systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Treating systolic blood pressure
Lifestyle changes are recommended as the first step in treating any stage of systolic or high blood pressure. These changes may include:
- eliminating unhealthy diets, such as excess sugars and saturated fats
- eating more heart-healthy meals such as lean meats, fish, fruits and vegetables, and whole grains
- hitting back on sodium in your food
- drinking more extra water
- getting regular physical activity
- quitting smoking
- managing a healthful weight
- decreasing alcohol consumption
- managing stress
- controlling your blood pressure usually
Treating low diastolic blood pressure
Treatment for normal diastolic blood pressure based on the situation. If medicines produce low blood pressure, your specialist may increase your dosage of that medicine or stop your treatment with it.
If a disease produces your low diastolic blood pressure, your specialist might appoint a medicine to heal the disease.
|
Risk factors of blood pressure |
|
| Systole | Diastole |
| Relatives with high blood pressure, Cardiovascular disease | High blood pressure medications |
| Overweight or obese | Diuretics |
| Diabetes | Nitrates |
| High cholesterol | Anxiety or depression medications |
| Kidney disease | Erectile dysfunction treatment |
| Too much alcohol, smoking, or tobacco | Thyroid problems |
| Too much sugar, salt, or more | Diabetes |
What are the medicines for blood pressure?
Different medicines can be used for blood pressure; consult the doctor or specialists to get your medicines. Do not practise any medicines without the doctor consultation.
Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Isosorbide Dinitrate
- Digoxin
- Clopidogrel
- Losartan + Hydrochlorothiazide
- Propranolol
What are the complications to get diastolic or systolic blood pressure?
There are different complications you may face to get diastole vs systole blood pressure. Here are the different complications you may face that includes:
Systolic blood pressure
It will be hard to notice the blood pressure symptoms as it is called a silent killer because it simply breaks your blood vessels and organs. Different complications of high blood pressure can lead to:
- heart stroke
- heart failure
- vision difficulties
- vision damage
- heart attack
- kidney infection
- sexual dysfunction
- aneurysm
Diastolic blood pressure
Normal diastolic pressure lead to low blood pressure that causes different complications that can include:
- dizziness
- fainting
- seizures
- chest discomfort
- falling
- lack of balance
- vomiting
- dryness
- inability to think
- headaches
- blurred image
- tiredness
- superficial breathing
- shortness of breath
- clammy skin
How to check blood pressure at home?
Checking blood pressure frequently at home using a blood pressure monitor is essential for many different people, especially if you have hypertension or hypotension. Tracking at home helps you to know while your treatment is working or not.
Consult your specialists to get an easy to use blood pressure monitor. While using the blood pressure monitor, adjust the cuff properly to get the proper readings. Consult the specialists to get an idea of how to use the blood pressure monitor accurately.
You additionally can practice a wrist blood pressure monitor, although they often aren’t as precise. Understand the regulations method that comes with the device to get assured you are utilising it accurately.
No matter which type of blood pressure monitor you have, it’s a reliable approach to get it to your doctor’s appointment. You can examine its reading to the figures your doctor understands. Avoid coffee, smoking, and exercise for at least 20 minutes before the test.
Summary
Diastole and systole blood pressure can vary from person to person. Consult the doctor to get an appointment and daily recommendation. Also, maintain your daily life with a healthy diet and physical activity.

 Login/Register
Login/Register









.png)
Be the first to comment on "Systolic and Diastolic: Risks, Complications, and Treatments of Blood Pressure"