Cervical cancer is a sign of the person’s possibility of survival for at least 5 more years as per the cancer stage. During the treatment, avoid visiting public places so as not to get an infection. Avoid going grocery or drugstore; provide yourself with emergency medicines through an online pharmacy in the Philippines to avoid crowded places; also, try to use a private cab while visiting the clinics. This helps you to be safe and protected.
Table of Contents
Cervical cancer definition
Cervical cancer rises in the Cervix, a hollow cylinder that joins the deeper part of a woman’s uterus to her vagina. Most cancers are found in cells on the outside of the Cervix. Multiple strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), an STDs, perform a role in producing most cervical cancer. You can overcome your chance of developing cervical cancer by having screening tests and getting a vaccine that fights against HPV infection.
Cervical cancer symptoms
In the beginning stages of cancer, an individual may feel cervical cancer early symptoms appear in the body. The most usual symptoms are:
- cervical cancer bleeding during periods or after intercourse
- bleeding during post-menopausal women
- pain during sexual intercourse
- vaginal release with a pungent smell
- vaginal release tinged with blood
- pelvic discomfort
Types of cervical cancer
The type of cancer that you have serves to plan your prognosis and prescription. The main types are:
- Squamous cell carcinoma. This type of cancer therapy starts in the thin, flat cells overlying the outer part of the Cervix, which extends into the vagina.
- Adenocarcinoma. This occurs in the column-shaped epithelial cells that follow the cervical channel.
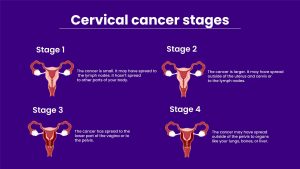
Stages of cervical cancer
The cervical cancer staging at which an individual suffers a cervical cancer treatment can better show their possibilities of survival for at least 5 more years. These are average continuation rates and do not appeal to everyone. In some cases, treatment is intense up to stage 4.
- Stage 1: In initial stage 1, the probability of surviving at least 5 years is 93 percent, and in end-stage 1, it is 80 percent.
- Stage 2: In initial stage 2, the percentage is 63 percent, dropping to 58 percent by staging 2.
- Stage 3: During this stage, the possibilities decrease from 35 percent to 32 percent.
- Stage 4: Patients with stage-4 cancer have a 15 to 16 percent probability of lasting another 5 years.
Risk factors for cervical cancer
There are different other factors available that play a role. Several risk factors have been recognized that raise a woman’s chance of growing cancer:
- Smoking
- HIV infection
- Immune system destruction
- Past or current Chlamydia disease
- Weight gain
- Long-term usage of oral contraceptives pills
- Owning three or more extra full-term reproductions
- Owning first full-term fertility before age 17
- Family records of cancer
Cervical cancer treatment
Cancer is highly treatable if you detect it shortly. Sometimes these treatments are linked to delivering them longer effectively.
The four central cancer treatments are:
- surgery
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- targeted therapy
Surgery
The purpose of surgery is to eliminate as much cancer as possible. Sometimes the specialist can exclude only the area of the Cervix that carries cancer cells. For cancer that’s extra widespread, surgery may include raising the Cervix and different organs in the pelvis.
Radiation therapy
Radiation destroys cancer cells by applying high-energy X-ray emissions. It can be performed throughout a device outside the body. It can also be performed inside the body, practicing a metal pipe in the uterus or vagina.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy practices medicines to ruin tumor cells entirely in the body. Specialists perform this procedure in cycles. You’ll undergo chemo at any time.
Targeted therapy
Avastin is a more innovative medicine that acts separately from chemotherapy and transmission. It prevents the growth of increased blood vessels that support cancer spread and last. This medication is usually administered collectively with chemotherapy.
Cervical cancer preventions to follow
To reduce your risk of cancer:
- Consult your specialist about the HPV vaccine. Getting a cervical cancer vaccine to inhibit HPV infection may overcome your chance of cancer. Gardasil 9 is an HPV vaccine licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and can be practiced for girls and boys.
- Hold regular Pap tests. Pap tests can identify precancerous states of the Cervix to be controlled or used to inhibit cancer.
- Practice protected sex. Overcome your chance of cancer by using protection to prevent STIs, including a condom every time you have sex and restricting the number of sexual partners.
- Quit smoking. If you don’t smoke, don’t begin. If you do smoke, speak to your specialist about tactics to improve you to quit smoking.
Summary
Cervical cancer was once a leading cause of death among American women. That has changed since screening tests became widely available. So if you are facing any symptoms, consult your specialist or doctor to get your treatment done in the early stages.

 Login/Register
Login/Register









Be the first to comment on "Cervical Cancer: What is it, Symptoms, Stages, Treatment, And More"