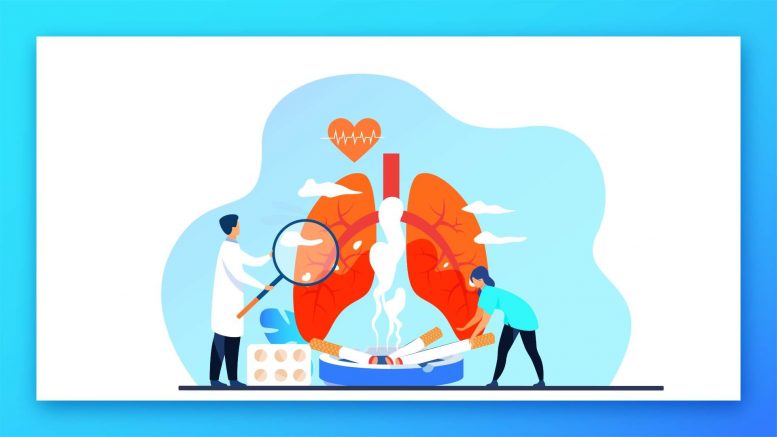
People who smoke may suffer from a risk of lung cancer, but lung cancer doesn’t mean it only occurs to the people who are smoking; it may occur to normal people also. The risk of lung cancer increases as the number of cigarettes a person is smoking in a day. Even after smoking so many times in a day, you can gradually decrease your risk of developing lung cancer if you quit smoking. So to prevent lung cancer, quit smoking and make others aware of quitting smoking to support lung cancer awareness everywhere in the nation.
If you’re a lung cancer risk, consult the specialists soon so that together you can decide whether lung cancer screening is right for you or not. Start taking treatment and medicine in the early stages as per the doctor’s recommendations. Along with the treatment, you can order cancer medicine online through a pharmacy in the Philippines so that you don’t miss any day without treating lung cancer. People with an increased chance of lung cancer may estimate annual lung cancer screening using low-dose CT scans like CT scans and other diagnosis treatments are part of lung cancer treatment to treat more precisely.
Table of Contents
What is lung cancer?
Cancer produces variation in cells to develop too quickly without dying off. Therefore, many different cells die during the life cycle of the particular stage. In the lung cancer stages, however, the cells exceed to grow and double the cell. As a result, the tumors develop, which leads to cancer issues. The two major types of lung cancer are small-cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.
It identifies by depending on how they seem under a microscope. For example, non-small cell lung cancer is more well-known than small cell lung cancer. As discussed before, cigarette smoking, and exposure to smoke, inhaled drugs, or other toxins vapors may raise lung cancer risk.
Lung cancer types:
There are two different lung cancer types: non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. They vary in the measurement of the cell, as seen under a scope.
1. Non-small cell lung cancer
According to the report, around 84% of lung cancer cases are non-small cells. There are three subtypes:
- adenocarcinoma
- squamous cell cancer
- large cell carcinoma
2. Small cell lung cancer
According to clinical research, around 13% of lung cancer cases are in small cells. In addition, this type of lung cancer cell develops even more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer. People may not observe the causes and treatment options for small cell lung cancer without healthcare specialists. Consult a doctor immediately after observing any health issues.
Lung cancer symptoms and signs :
People may not observe in the starting lung cancer stage until the symptoms become more severe and recognized. If symptoms start developing, they can easily match respiratory infection. If lung cancer is recognized in your body, start regular screening of lung cancer as per the doctor recommendations.
Some early lung cancer symptoms include:
- chest pain
- breathing issues
- wheezing issues
- expanding lymph nodes in the center of the chest
- a lingering cold that may rise to get more acute
- changes to the individuals’ voice, such as dizziness or hoarseness
- repeated chest infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia
In time, an individual may additionally experience more severe lung cancer symptoms and signs, such as:
- critical chest pain
- fatigue
- appetite loss and weight loss
- headaches
- choking up blood
- blood clots
- bone pain
- bone fractures
How does smoking cause lung cancer?
Specialists consider smoking to produce lung cancer by destroying the cells that fill the lungs. So when you breathe tobacco smoke, which carries complete cancer-producing elements, befalling in the lung tissue begins almost instantly.
In the beginning, your body may be capable of repairing this loss. However, with specific repeated appearance, normal cells that overlay your lungs are frequently infected. Over time, the damage affects cells to function abnormally, and ultimately, cancer may occur or start growing speedily.
What are the stages of lung cancer?
The different lung cancer stages define how considerably it has spread throughout the body, and it’s critical. In addition, the stages of cancer advise healthcare specialists and individuals to choose a proper plan for treatment.
The most basic lung cancer stages include:
- localized: It means the cancer is within a confined area
- regional: Cancer has grown to nearby tissues or lymph nodes
- distant: Distant indicated cancer has developed to other parts of the body
1. Stages of non-small cell lung cancer
Healthcare experts considerably used tumor size and developed to explain the lung cancer stages of non-small cell lung cancer, as results:
- hidden stage: Cancer does not seem on imaging scans; only cancerous cells strength develop in the phlegm or mucus.
- Stage 0: There are unusual cells simply in the head layers of cells outlining the airways.
Primarily there are 4 stages of lung cancer are:
- Stage 1: A tumor is started in the lung, although it is 4 cm or under and has not grown to other body portions.
- Stage 2: The tumor is 7 cm or below and might have grown to nearby muscles and lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: Cancer has increased to lymph nodes and touched other lung and circling areas.
- Stage 4: Cancer has grown to different parts of the body, such as the bones or brain.
2. Stages of small cell lung cancer
- The stages are insufficient and unrestricted, and they belong to whether cancer has developed inside or outside the lungs.
- Cancer hits particularly one side of the chest in the restricted stage, though it might previously be present in circling lymph nodes.
- Throughout, one-third of the individuals with this stage assume they have cancer in the confined stage. Healthcare specialists can operate it with radiation therapy in a particular area.
- In the far-reaching stage, cancer has expanded beyond the one side of the chest. It may harm the opposite lung or other body parts.
- Approximately two-thirds of people with small cell lung cancer discover they have it previously in the far-reaching stage.
Non-small cell lung cancer |
Small cell lung cancer |
|
Localized: 63% Regional: 35% Distant: 7% Overall : 25% |
Localized: 27% Regional: 16% Distant : 3% Overall : 7% |
According to the studies, the possibility of surviving for 5 years or longer after undergoing a lung cancer diagnosis, the percentages indicate the possibilities of a person sustaining with lung cancer associated with surviving without lung cancer.

 Login/Register
Login/Register









Be the first to comment on "Lung cancer: Types, Stages, Causes, and More"